In an era characterized by rapid technological evolution, trust has emerged as the cornerstone of successful AI adoption. Trust in AI systems is the dynamic state of mind that determines whether users feel confident in the decisions made by these systems. When we refer to trust in AI, we are talking about a complex relationship that derives from consistent performance, reliability, and ethical considerations. As industries expand their dependency on artificial intelligence, this sense of trust directly influences user acceptance, investment strategies, and regulatory support. The importance of trust in AI is also mirrored in our daily interactions with technology, where expectations of safety and transparency become paramount as users navigate systems that influence decision-making at all levels (ref: CMU SEI Blog ).
Additionally, trust acts as the form of social currency that technology companies need to build sustainable relationships with consumers. Companies that invest in trustworthy AI find themselves rewarded with customer loyalty, and a competitive edge in an increasingly crowded market. Moreover, public confidence is bolstered when AI systems are both effective and safe, creating an environment where users feel secure in relying on automated processes for critical tasks. Investing in trust is not simply a matter of fulfilling regulatory requirements—it is a proactive strategy that sets the stage for long-term success in the digital landscape. Each stakeholder, from developers to end users, plays a vital part in fostering an ecosystem where technology and trust go hand in hand.
Furthermore, the ramifications of mistrust can be severe. Without adequate trust mechanisms, users may quickly abandon digital platforms, governments might impose harsh regulations, and investors could lose faith in innovative prospects. Therefore, the establishment and cultivation of trust are not optional but necessary for the future trajectory of AI systems. Each success story in AI is fundamentally intertwined with the level of trust it has managed to build among its users, thereby making it a crucial business imperative.
Foundations of Trust: Calibrated Confidence and Trustworthiness Components
Building trust in AI involves much more than implementing effective algorithms. It is about achieving calibrated trust, where the user’s confidence is in perfect balance with the actual performance and reliability of the system. Calibrated trust is not static but changes with user experiences, making it essential for developers to continuously monitor and adjust their systems. By building a system that inherently calibrates user expectations, developers can ensure that trust is both earned and maintained over time.
- Calibrated Trust:
Calibrated trust refers to aligning user expectations with the inherent capabilities of an AI system. This means that end users need to have accurate perceptions of how reliable, safe, and intuitive a system truly is—thereby enabling them to engage without undue scepticism. This kind of trust is crucial because it directly influences user behavior; knowing precisely what to expect minimizes the risk of overreliance or misinterpretation of AI output. The calibration process is dynamic, designed to adapt in real-time based on shifts in system performance and external inputs. As psychological research implies, trust is a personal and transient state that can only be properly addressed when correctly measured and appropriately nurtured (ref: CMU SEI Blog ).
- Components of Trustworthiness:
Trustworthiness in AI is a multi-faceted concept that comprises several indispensable components. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has outlined essential aspects including validity, reliability, safety, security, and resiliency. These components must be carefully balanced alongside accountability, transparency, explainability, and privacy measures to create a robust trust framework. Implementing these elements encourages user confidence; when an AI system demonstrates transparency and fairness, users are more inclined to embrace it as a viable tool in solving real-world problems. Hence, organizations need to focus on these core components to enhance not only the ethical stance of their systems but also the satisfaction among their users (ref: CMU SEI Blog ).
- Measuring Trustworthiness:
Evaluating the trustworthiness of any AI system is an intricate process that employs both qualitative and quantitative measures. Instruments such as functional performance evaluations, user experience studies, and rigorous testing protocols are utilized to assess how well the system performs against set criteria. However, certain personal perceptions of trust can be elusive to measure because they are inherently subjective. Such comprehensive evaluation approaches allow creators to bridge the gap between technical performance and user satisfaction. It is crucial, therefore, for organizations to deploy multiple measures in tandem to capture the full spectrum of trust-building dynamics (ref: CMU SEI Blog ).
Pioneering Trust in Technology: Best Practices for Organizations
The trajectory of building trust in technology is supported by a suite of best practices that various organizations can adopt in order to ensure long-term success. Among these, prioritizing trust over mere functionality stands out as a critical point that modern companies are beginning to embrace. By dedicating resources to demonstrate true commitment to ethical practices, tech companies build a more substantial rapport with their users. Both the corporate investment community and regulatory authorities are keenly observing this trend as a requisite for technological innovation and adoption.
- Prioritizing Trust:
Trust should be placed at the heart of any technology strategy. A company that prioritizes trust not only attracts loyal customers, but it also lays the foundation for robust long-term growth. Such companies make substantial efforts to protect customer data and foster a transparent business environment. By sharing clear policies and procedures about how user data will be safeguarded, these organizations dispel fears and rumors that often plague new technologies. With a clear demonstration of commitment to user rights and data protection, trust becomes a key driver of both user engagement and investor confidence (ref: BDO Insights ).
- Adhering to Global Standards Like ISO 42001:
Adopting internationally recognized standards, such as ISO 42001, reinforces accountability and responsibility in technological practices. ISO 42001 sets out robust criteria for responsible AI use by covering elements such as data quality, bias mitigation, and cybersecurity. Conforming to these standards not only instills confidence among users but also serves as a reputable accreditation that governments and regulatory bodies can endorse. Through adherence to such standards, an organization demonstrates that it is serious about creating safe, ethical AI systems, thus paving the way for increased market penetration and customer engagement (ref: BDO Insights ).
- Continuous Improvement through Transparency:
Transparency is not a one-time effort; it is a continuous journey that requires ongoing dialogue with stakeholders. Companies should be open about the design, limitations, and functioning of their AI systems. Regular, accessible updates on performance, challenges, and improvements help instill trust over time. This approach resonates well with a user base that values clarity and accountability, encouraging sustained engagement and loyalty (ref: CMS Wire ).
Embracing Ethical AI: Paving the Way for Transparent and Responsible Technology
One of the most compelling approaches to building trust in AI systems is through ethical AI practices. To many, ethical AI represents the embodiment of fairness, accountability, and accountability in technology. The advocates for ethical AI argue that beyond pure performance, it is the ethical framework that will determine long-term acceptance and integration into our social fabric. This framework requires developers and stakeholders to address operational transparency, unbiased data processing, and comprehensive privacy safeguards.
- Ethical Considerations in Practice:
Ethical AI emphasizes not just the end result, but the journey taken to achieve that outcome. Organizations are tasked with embedding fairness and balance into every layer of their system. The deliberate mitigation of bias in data and algorithms helps prevent unfair outcomes and ensures inclusivity amongst diverse user demographics. Such commitment transforms the relationship between technology and its users, heralding a new era where AI decisions are both trusted and respected (ref: Lumen Alta ).
- Fairness and Bias Mitigation:
The presence of bias in AI systems can significantly hamper trust and credibility. Implementing measures to address these biases involves detailed data audits and continuous algorithm evaluations. Organizations must work proactively to study the data sources and adjust their algorithms by incorporating diverse datasets to ensure balanced and equitable outcomes. Such attention to fairness does not merely highlight ethical commitments but also enhances public trust in AI-driven decisions (ref: Lumen Alta ).
- Transparency and Accountability in AI Decision-Making Processes:
When the decision-making process behind AI outcomes is transparent and explainable, users are more likely to trust the system. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques help demystify how and why certain decisions are made, which is particularly important in high-stakes environments such as healthcare or finance. This assurance builds stakeholders’ confidence that the AI is not a black box but a well-understood tool that can be continuously refined. By making information accessible and engaging in an honest narrative about system functionalities, organizations set a cultural norm that encourages enduring trust in technology (ref: Lumen Alta ).
Transparency in AI: The Roadmap to Gaining End-User Confidence
Transparency is increasingly recognized as the linchpin for securing trust in modern AI implementations. A transparent AI system openly communicates its methodologies, limitations, and decision-making processes. This not only reassures users of the system’s integrity, but it also empowers them with the knowledge required to engage critically with automated decisions. In a world where technological missteps are frequently highlighted, a transparent approach can negate skepticism by pre-emptively addressing concerns. Companies that prioritize transparency position themselves as accountable and reliable partners in the digital age, paving the way for broader acceptance and continuous innovation.
- Emphasizing AI Transparency:
Transparency in AI means that everything from data handling practices to the intricacies of the algorithms is communicated clearly. User interfaces that explain decision-making processes allow users to participate in a dialogue with the technology, addressing concerns in real-time. This clarity helps mitigate common fears related to misuse or manipulation of technology, creating a partnership between developers and users. The clarity offered by this transparency enables immediate feedback mechanisms, ensuring that any identified discrepancies can be corrected swiftly (ref: CMS Wire ).
- Case Study: Apple’s Privacy-Centric Approach:
A prime example of the power of transparent practices is Apple. The tech giant has built a reputation for prioritizing user privacy by incorporating features like on-device processing for Siri and employing differential privacy techniques. Their strategy has successfully earned user trust and loyalty because they openly communicate how they protect user data. Such innovations go a long way in reassuring customers that their privacy is sacrosanct while also showcasing that high-performance and secure systems can go hand in hand (ref: CMS Wire ).
Maximizing User Engagement in AI Applications
User engagement stands as a pivotal aspect of creating successful AI systems. By providing personalized experiences and clear explanations of AI-driven decisions, companies can reduce hesitancy and foster active user interaction. Encouraging users to trust and engage more deeply with AI systems has ramifications that extend beyond functional efficiency; it underlines a commitment to enhancing everyday life. When users see value, convenience, and transparency in AI-powered interfaces, their willingness to adapt and rely on technological solutions increases dramatically. The interplay between technology and user engagement fosters an environment where iterative improvement is driven by real-time feedback, ensuring the product evolves in line with user expectations.
- Personalized User Experiences:
AI is poised to revolutionize how content is delivered by tailoring user experiences based on past interactions and predictive analytics. Personalized content algorithms not only make applications more efficient but also help in building a tailored customer journey that resonates with diverse user needs. This degree of customization is scientifically shown to increase user retention rates and bolster satisfaction by presenting users with information and services that feel almost intuitively tuned to their preferences. Such personalization acts as a key trust-building mechanism, as users are more likely to engage with technology that appears to understand them on a personal level (ref: Flexum.io ).
- Explainability Enhances Engagement:
Explainable AI goes a step further by educating users on how automated decisions are made. When a system provides straightforward reasons behind its recommendations or actions, it invites users to feel more secure and involved. This demystification encourages ongoing engagement because it eliminates the fear of the unknown, a common deterrent to the adoption of AI systems. As users become more familiar with the inner workings of an AI process, trust deepens, and their willingness to interact with the technology increases (ref: CMS Wire ).
- Feedback Mechanisms and Continuous Improvement:
Building robust feedback loops between users and the system serves a dual purpose. It not only informs the development team about potential issues or areas for improvement but also communicates to users that their opinions are valued. The ability to listen to end-user critiques and act on them reinforces a transparent relationship between the consumer and the application provider. Continuous upgrades based on this direct feedback make the system more adaptive, resulting in improvements that cater directly to user needs and foster long-lasting trust (ref: Flexum.io ).
A Data-Driven Look: Measuring Trust and Engagement in AI
In today’s data-centric world, quantifying trust and engagement is almost as important as creating it. Organizations are increasingly resorting to innovative methods for capturing user sentiments and measuring system performance. The integration of qualitative studies with quantitative measurements is transforming how trust is assessed in AI applications. For example, surveys and UX studies can be combined with algorithm performance metrics to offer a comprehensive view of trustworthiness. This quantitative backing not only strengthens the credibility of trust-building strategies but also aids in fine-tuning the system continuously to meet evolving user expectations.
- Metrics for Trustworthiness:
Measuring trust involves several essential metrics including reliability scores, response times, and error rates. These metrics provide a baseline for comparing system performance across different environments. Trust indicators such as these are often paired with user feedback to obtain a more multifaceted view of system performance. The data collected forms the foundation for implementing iterative improvements and adapting algorithms to meet the nuanced needs of end users. Combined with qualitative insights, these metrics create a robust framework for understanding and enhancing trust (ref: CMU SEI Blog ).
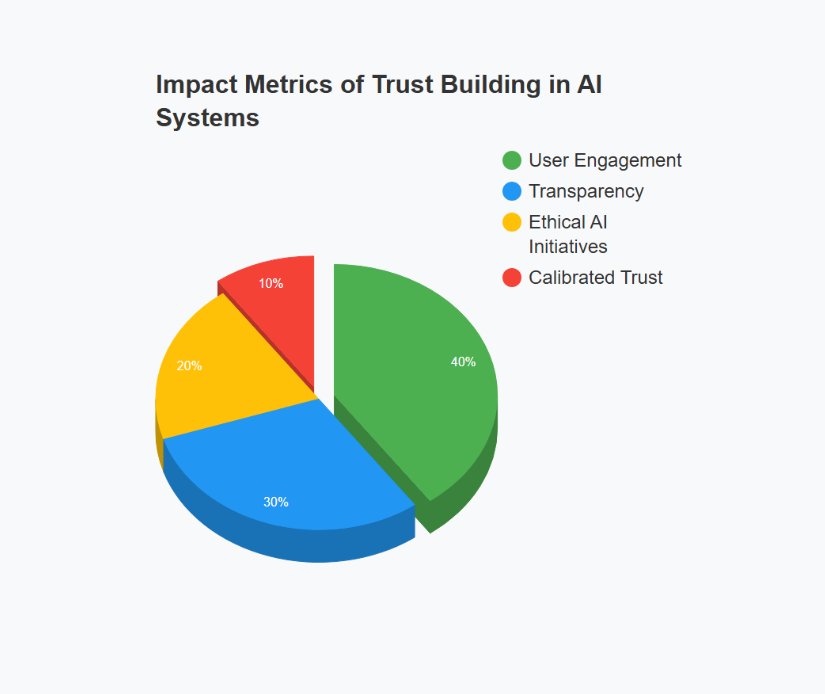
- Charting the Impact of Trust-Building Practices:
One way to visualize the influence of various trust-building metrics is through engaging charts and graphs. For instance, organizations can track user engagement rates, satisfaction scores, or the frequency of positive user interactions over time. Such data visualization not only highlights the progress made but also illuminates areas in need of further investment. By translating numerical data into visual insights, companies can better communicate the success of their trust-enhancement strategies to a broader audience (ref: CMS Wire ).
The Future Landscape: Fostering a Culture of Trust and Continuous Engagement
Looking ahead, the evolution of AI systems is intricately linked with the capacity to cultivate lasting trust among users. As technology continues to advance, it is inevitable that the expectations regarding transparency, ethical behavior, and user-centric design will only intensify. Emerging trends such as decentralized AI platforms, enhanced privacy technologies, and ubiquitous user engagement tools are set to redefine how trust is both constructed and maintained. Forward-thinking organizations are already investing in the research and development of these innovations, anticipating a future where accountability is embedded at every level of the AI lifecycle.
- Emerging Technologies and Trust Paradigms:
As we step into a future shaped by increasingly advanced AI architectures, the focus on trust remains unshaken. Innovations such as blockchain for data verification, autonomous decision auditing systems, and decentralized AI networks are leading the way in creating ecosystems that are transparent by design. These technologies provide a new layer of accountability and traceability, allowing users to verify the integrity of AI decisions in real-time. The convergence of these innovations is poised to redefine the digital trust landscape, making it more robust and resilient for future challenges (ref: CMS Wire ).
- Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Feedback:
A proactive culture that thrives on continuous user feedback is essential for long-term trust in AI systems. Organizations that nurture a two-way communication channel not only keep abreast of emerging needs but also demonstrate that every user opinion matters. It is through this ongoing dialogue that systems evolve and adapt, ensuring that technology remains relevant and reliable. With trust as the glue that binds user interactions, a culture of continuous improvement is not just beneficial—it is indispensable for future innovation (ref: Flexum.io ).
- Transparent Reporting and Accountability Frameworks:
To wrap accountability into the fabric of AI operations, companies should consider regular transparency reports that detail system performance, updates, and challenges. These reports serve as a testament to the organization’s commitment to maintaining high ethical standards while driving continuous improvement in AI processes. Sharing such comprehensive updates helps demystify the technology, making users an active part of the journey rather than passive end-recipients. In a rapidly evolving tech landscape, such ongoing communication is a sure way to nurture enduring trust (ref: Lumen Alta ).
Are You Ready to Transform Your Business with Trustworthy AI?
Reinventing the way we interact with technology begins with ensuring our AI systems are not just advanced, but truly trustworthy. With ethics, transparency, and continuous user engagement at the forefront, the future of AI is built on solid foundations that promise both innovation and accountability. As you reflect on the evolving landscape of AI, consider how these trust-building strategies could redefine your organizational goals.
Now is the time to take action: embrace ethical AI, invest in transparency, and create technology that users not only rely on but wholeheartedly trust. How will you begin your journey toward fostering legendary trust in your AI systems?
References
- https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/blog/contextualizing-end-user-needs-how-to-measure-the-trustworthiness-of-an-ai-system/
- https://www.bdo.com/insights/industries/technology/building-trust-should-be-a-top-priority-for-tech-companies-heres-why
- https://lumenalta.com/insights/ethical-considerations-of-ai
- https://flexum.io/post/ai-in-apps-user-engagement-boosters
- https://www.cmswire.com/ai-technology/ai-transparency-and-ethics-building-customer-trust-in-ai-systems/